A Global Map Of Roadless Areas And Their Conservation Status

The planet s remaining large and ecologically important tracts of roadless areas sustain key refugia for biodiversity and provide globally relevant ecosystem services.
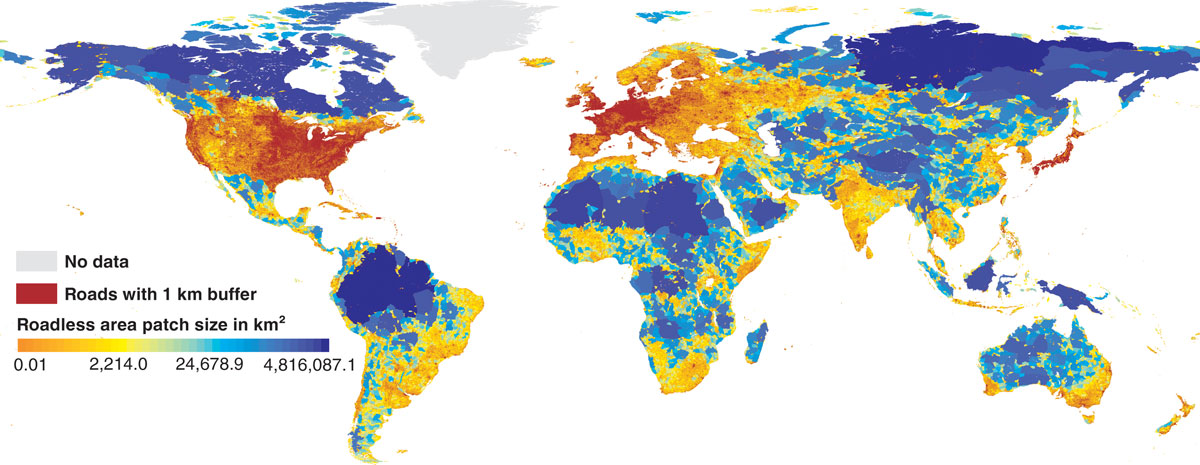
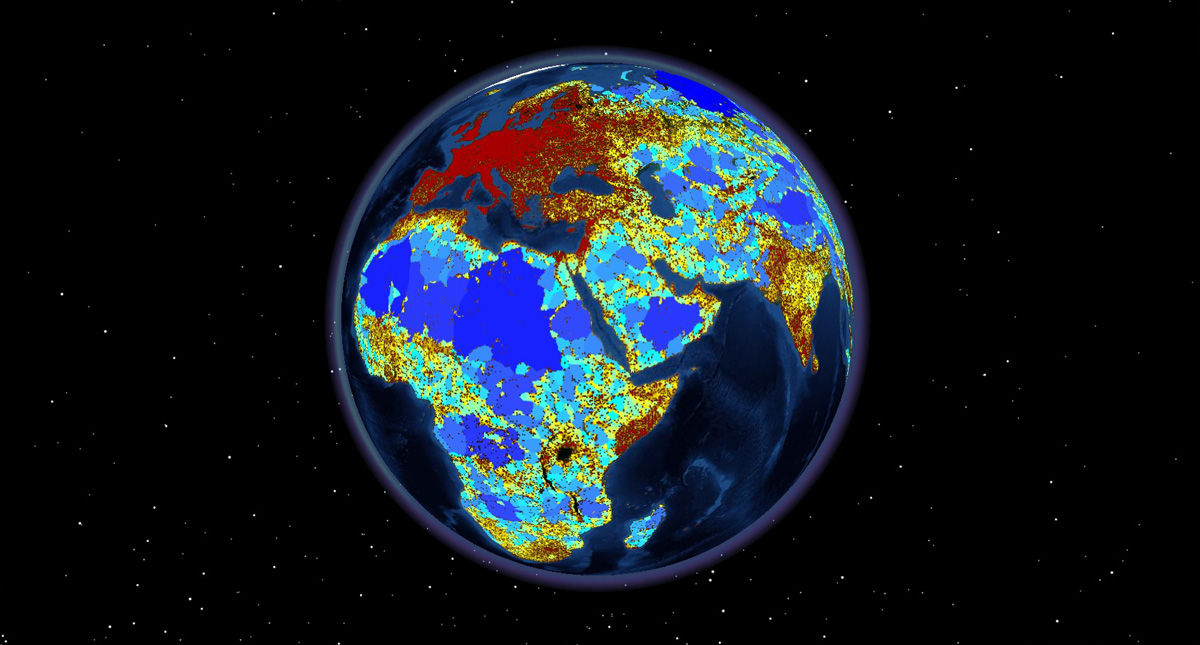
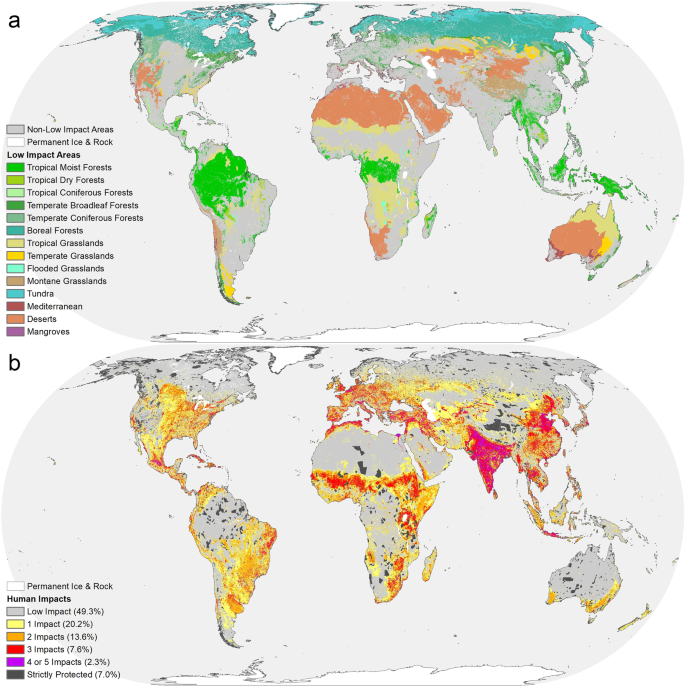
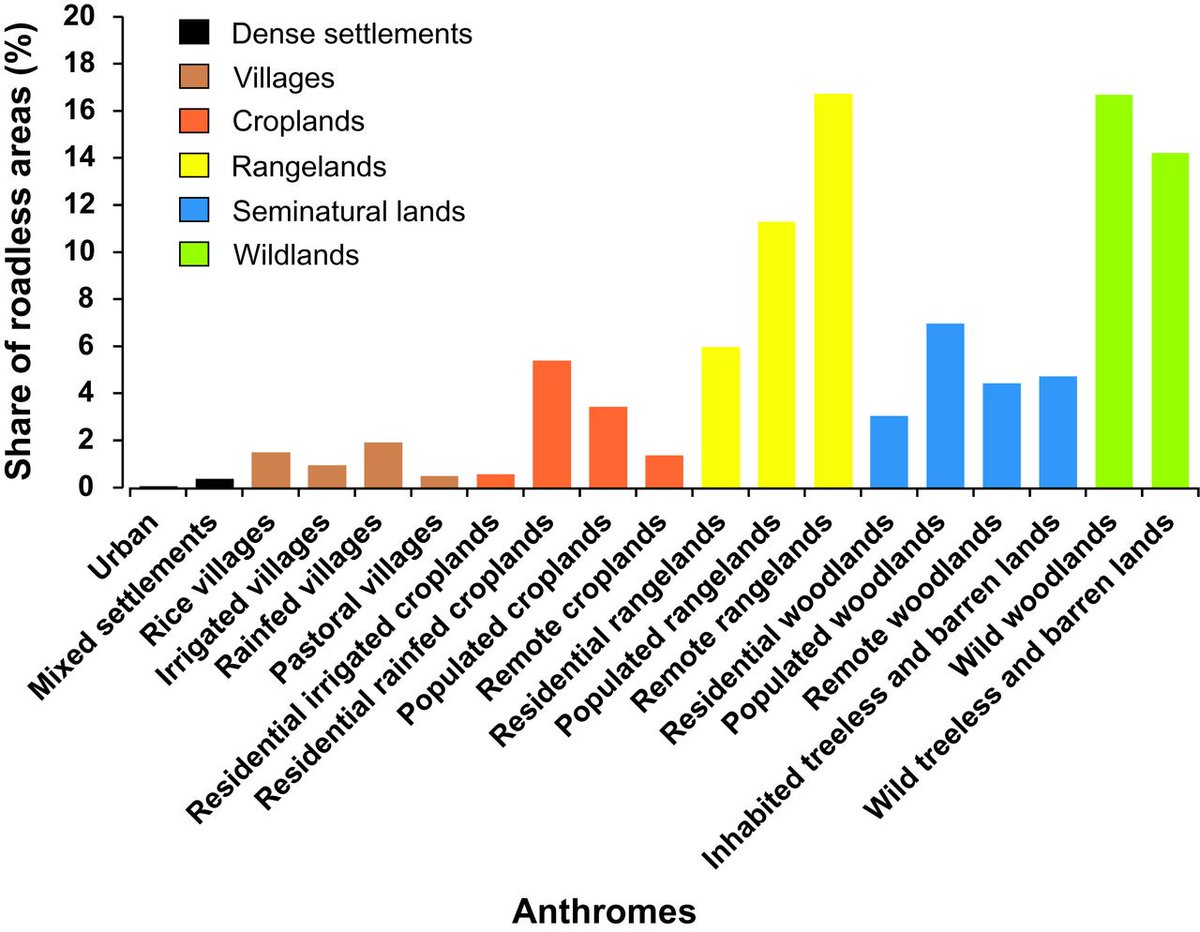
A global map of roadless areas and their conservation status. Cataloged roads across the world. More than half of them are smaller than 1 km 2. The planet s remaining large and ecologically important tracts of roadless areas sustain key refugia for biodiversity and provide globally relevant ecosystem services. In their report a global map of roadless areas and their conservation status 16 december 2016 p.
Applying a 1 kilometer buffer to all roads we present a global map of roadless areas and an assessment of their status quality and extent of coverage by protected areas. The planet s remaining large and ecologically important tracts of roadless areas sustain key refugia for biodiversity and provide globally relevant ecosystem services. More than half of them are smaller than 1 km2. The planet s remaining large and ecologically important tracts of roadless areas sustain key refugia for biodiversity and provide globally relevant ecosystem services.
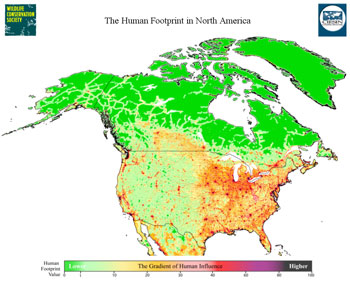
Applying a 1 kilometer buffer to all roads we present a global map of roadless areas and an assessment of their status quality and extent of coverage by protected areas. The planet s remaining large and ecologically important tracts of roadless areas sustain key refugia for biodiversity and provide globally relevant ecosystem services. Roads have made it possible for humans to access almost every region but this comes at a very high cost ecologically to the planet s natural world. A new global map of roadless areas shows that the earth s surface is shattered by roads into more than 600 000 fragments.
Applying a 1 kilometer buffer to all roads we present a global map of roadless areas and an assessment of their status quality and extent of coverage by protected areas. Roads have made it possible for humans to access almost every region but this comes at a very high cost ecologically to the planet s natural world.